Learn to identify the symptoms and causes of disc herniation, as well as effective treatment options for your condition.
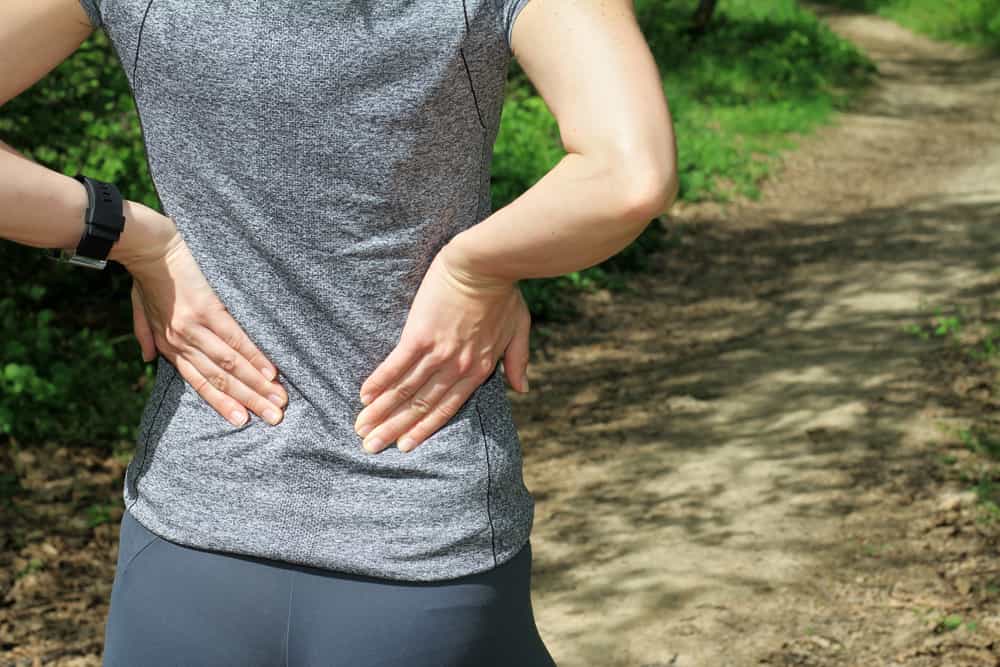
If you’ve ever suffered from back pain, you know how debilitating and disconcerting it can be — especially when you don’t know its source.
There are several common conditions that can cause discomfort in the back and neck, including disc herniation. This injury occurs when a cartilage disc between your vertebrae protrudes and puts pressure on the nearby nerves. If you’re suffering from pain in your neck or lower back, numbness or tingling in your extremities, and weakness in your back muscles, a herniated disc could be the cause.
Here’s how to determine if your symptoms are due to disc herniation, and how you can treat this painful condition.
WHAT IS DISC HERNIATION?
A herniated disc is caused by a tear or rupture in the outer ring of the cartilage that connects the spinal vertebrae. The gel-like center of this intervertebral disc becomes exposed and compresses the surrounding nerves. This usually results in pain, tingling, and weakness, though in some cases patients do not experience any symptoms. Most instances of disc herniation occur in the lower back, called the lumbar region, due to the pressure placed on this area by a range of movements.
A herniated disc can be the result of ordinary activities like coughing, sneezing, or sleeping in an awkward position. Prolonged sitting can be a contributing factor, especially if your posture is poor. On the other hand, disc herniation in a young, healthy patient is often caused by a traumatic injury. Athletes and weightlifters may also slip a disc while straining their backs.
Aging and natural degeneration can lead to disc herniation as well. Degenerative disc disease occurs when the discs between the vertebrae begin to dehydrate, weaken, and contract. This condition is usually the result of aging, and can be exacerbated by arthritis or osteoarthritis. As the intervertebral discs deteriorate and become less flexible, the outer ring is more likely to tear, resulting in herniation.
HOW TO TREAT A HERNIATED DISC
Most cases of disc herniation respond well to a conservative treatment plan that includes anti-inflammatory medication and physical therapy. A regular physical therapy regimen can help patients alleviate pain, restore flexibility, and rebuild muscles in the back and core. These exercises can also help to improve posture, lowering your risk of future injury.
If a herniated disc is compressing a nerve and causing pain, it can be treated with an epidural steroid injection to reduce inflammation and manage pain. This procedure can also improve your range of motion so that you can continue with your physical therapy plan.
While most herniated discs don’t require surgery, more severe cases can be treated by surgically removing some of the ruptured disc or fusing the vertebrae. Like most procedures, this surgery does present some risks for the patient, and is therefore best avoided in the majority of cases.
Patients suffering from disc herniation should visit an orthopedic specialist immediately. At New York Bone & Joint Specialists, back and neck expert Dr. Michael Y. Mizhiritsky will help diagnose your condition and develop an effective treatment plan. As a leading practitioner in electrodiagnostic testing, Mr. Mizhiritsky specializes in administering EMG tests to pinpoint the affected area and ensure that you experience the best possible results. Schedule an appointment today to get on the road to recovery.